
UTGB has several built-in tracks. In order to use them, specify track class name in your view file:
-track
-class: (track class name)ReadTrack in UTGB can be used to display genes, annotation on genome coordinates and read data written in BED, SAM and BAM (http://samtools.sourceforge.net/) formats. To do so, first you need to import these files using utgb import command.
BED is a common format for describing genes (including CDS, exon/intron regions) or locus annotations of genomes. You can obtain many useful BED files from UCSC's table browser, http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTables. For example, you can retrieve BED data of RefSeq gene sets by selecting refGene table and switch the output format to BED.
# create a BED database
$ utgb import db/refGene.bedAfter BED files are imported, edit your view file:
# Track for BED data
-track
-name: RefSeq Genes
-class: ReadTrack
-property
-path: db/refGene.bedWhen importing a BED file, the utgb import command creates an SQLite database file (suffixed with .sqlite) to accelerate database searches. When SQLite DB files corresponding to the input BED files are found, ReadTrack issues database queries to reads.bed.sqlite file instead of reading raw BED files.
db/sample.bed
track name="Item,RGB,Demo2" chr1 20000 70000 itemB 200 - 22000 69500 0 4 4330,1000,5500,15000 0,5000,20000,35000 chr1 20000 60000 cloneB 900 - 20000 60000 0 2 4330,3990, 0,36010 chr1 10000 50000 itemA 960 + 11000 47000 0,255,255 2 15670,14880, 0,25120 chr1 10000 50000 itemA 960 + 11000 47000 0 2 15670,14880, 0,25120 chr1 10000 50000 itemC 960 + 11000 47000 0 chr1 10000 50000 itemD 960 + 11000 47000 0,255,0 chr22 20100000 20100100 first chr22 20100200 20100300 second chr22 20100400 20100500 thirds chr7 127472363 127473530 Pos2 200 chr7 127472363 127473530 Pos2 200 + chr7 127472363 127473530 Pos2 200 + 127472363 127473530 chr7 127472363 127473530 Pos2 200 + 127472363 127473530 255,0,0
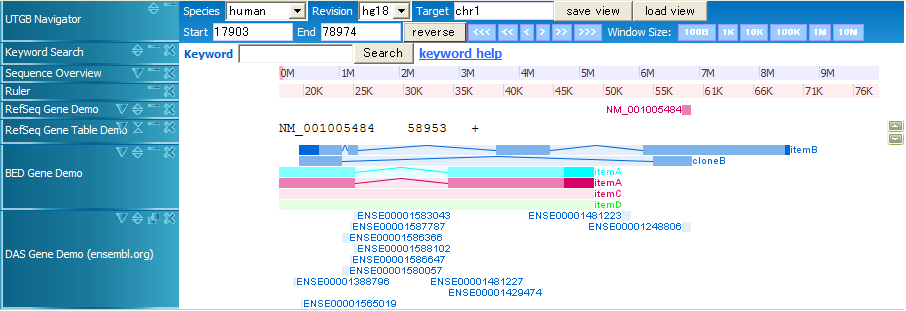
In BED files, the first six parameters (chr, start, end, name, score, strand) are required, and the other parameters are optional. By using RGB color fields, you can change the colors of BED entries.
SAM format is commonly used to describe alignment results of next-generation sequencer reads (e.g., Illumina, SOLiD, etc.). BAM format is a binary version of SAM. You can use the both formats in UTGB, but using BAM is recommended for the performance reason. To display read data in BAM files, you need .bai (BAM index) file to quickly locate file positions of the target window (chromosome name, start-end position). The bai files can be created when you import SAM files using UTGB, or samtools index command also can be used.
# create BAM (.bam) and BAM Index file (.bai) from the input SAM file
$ utgb import db/shortread.samAfter importing BED or SAM files, edit your view file:
# Track for BAM data. In this example, db/shortread.bam.bai file must be present.
-track
-name: Short Read
-class: ReadTrack
-property
-path: db/shortread.bamHere is a screenshot of displaying a BAM file of Illumina's paired-end library data: 
ReadTrack has severl properties to customize the visualization.
-track
-class: ReadTrack
-property
-path: db/sample.bam
-wig path: db/sample.bam.wig.sqlite
# pileup (draw individual reads) or coverage (shows read depth graph)
-layout: pileup
# Used when displaying read coverage
-window funcion: MAX
# pixel height of reads
-read height: 2
# horizontal margin between reads
-read margin: 1
# hide read name labels
-show labels: false
# When true, the lower the base quality, the more translucent the base color becomes
-show base quality: true
# Increase this number to show many reads (but consumes your browser memory and may slower the track drawing speed)
-num reads to display: 1000The wig path specifies wig database files of read depths, created from BAM files, which can be used to draw read depths when the number of reads contained in a query window are too many to display in the track.
To display bar graph data (e.g., read depth coverage, GC contents percentage data for each locus on genome), use WIG format http://genome.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/help/wiggle.html and WigTrack. First create an SQLite database file from a WIG file:
$ utgb import db/sample.wigThen, add the following configuration to your view file:
# Track for WIG data
-track
-name: bar graph
-class: WigTrack
-property
-path: db/sample.wig.sqlite
# Windowing function: MAX, MIN, MEDIAN or AVG
-window function: MAX
# max, min value of the y scale
-max value: 100
-min value: 0
# If true, adjust the y scale according to the displayed data
-auto scale: true
# To use log scale, set this parameter to true
-log scale: false
# Graph color. red, green, blue (0-255) and alpha (0-1)
-color: rgba(255,128, 128, 0.7)You can create read depth (coverage) graph data from BAM files by using utgb readdepth command.
$ utgb readdepth (BAM file) > db/readdepth.wigWig files are large in general. To save the storage space you can directly create wig databases of read coverage as follows:
$ utgb readdepth (BAM file) | utgb -t WIG import -o db/readdepth.wig.sqliteTo display a genome sequence as a track, you need to create a sequence database from a FASTA file. Commonly used FASTA files of reference genome sequences are available from UCSC's web site. For example, the fasta file of S. cerevisiae is available from http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/sacCer3/bigZips/chromeFa.tar.gz.
To create databases of FASTA files, do utgb import:
$ utgb import -t FASTA db/chromFa.tar.gz -o db/sacCer3.sqliteThe -t option specifies the input file format. The utgb import accepts both compressed archives (.tar.gz) and raw fasta files (.fa, .fasta).
The above import command generates a compressed FASTA database (SQLite file) db/sacCer3.sqlite. Next, add a track entry to your config/view/default-view.silk file:
-track
-name: Genome Sequence
-class: RefSeqTrack
-property
-path: db/sacCer3.sqliteThis will add a new track named Genome Sequence to your genome browser.
To add keyword search functionality, add the following track definition to your view:
-track
-class: KeywordSearchTrackTo add keyword entries to the database from the read names in BED/SAM/BAM files, use utgb keyword command:
$ utgb keyword import -r ce6 (BED/SAM/BAM file)-r option is used to associate sequence revision name and keywords contained in the input file. It is also possible to add your own keywords annotating loci in genome sequences. For details, see a help message in utgb keyword -help.
DAS track is for browsing DAS (Distributed Annotation System) data. Currently (utgb-shell version 1.2.3), browsing feature data is supported. Add the following Silk fragment to your view file, and edit the dasBaseURL property to specify the DAS server URL:
-track
-class: DASTrack
-name: DAS Track
-pack: true
-property
-type: image
-leftMargin: 100
-dasBaseURL: http://www.ensembl.org/das/Homo_sapiens.NCBI36.transcript/
-dasType: refGene